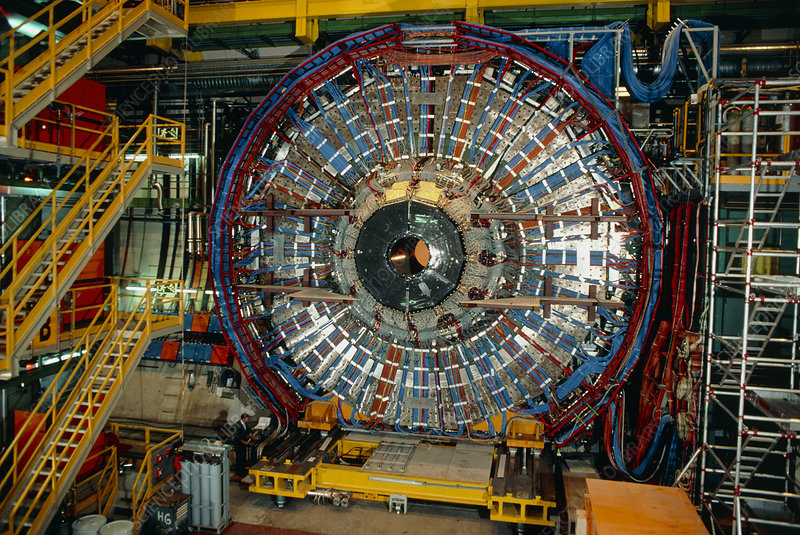
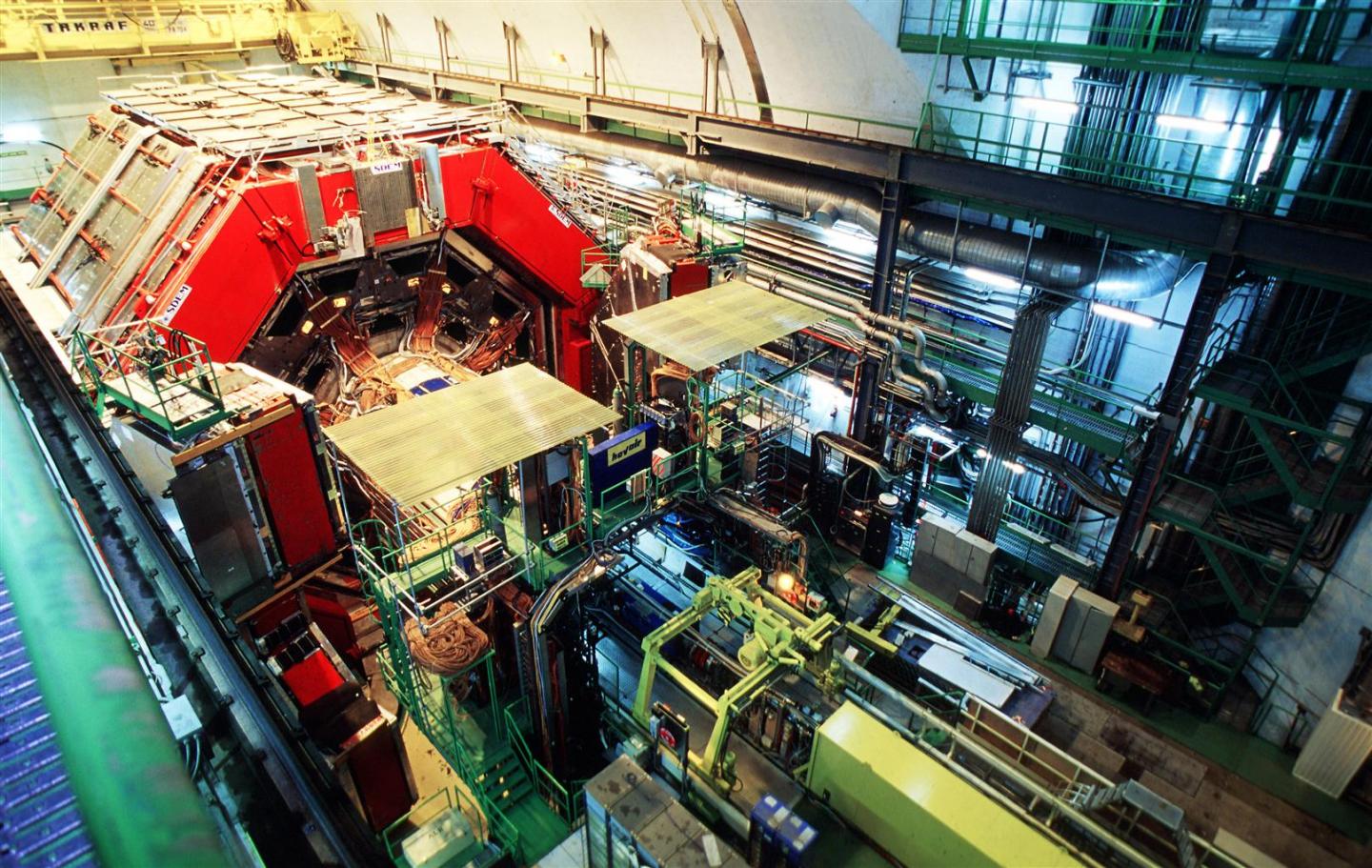
ATLAS Experiment
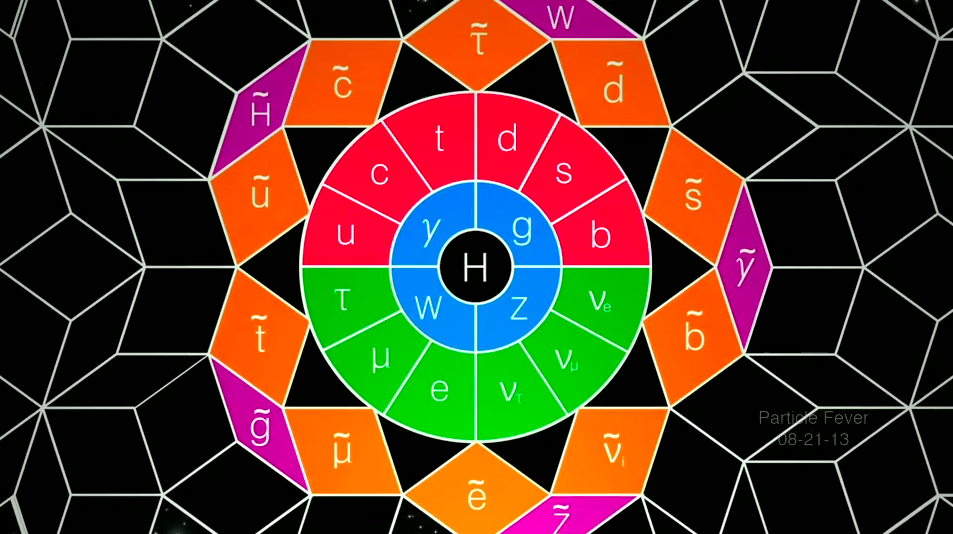
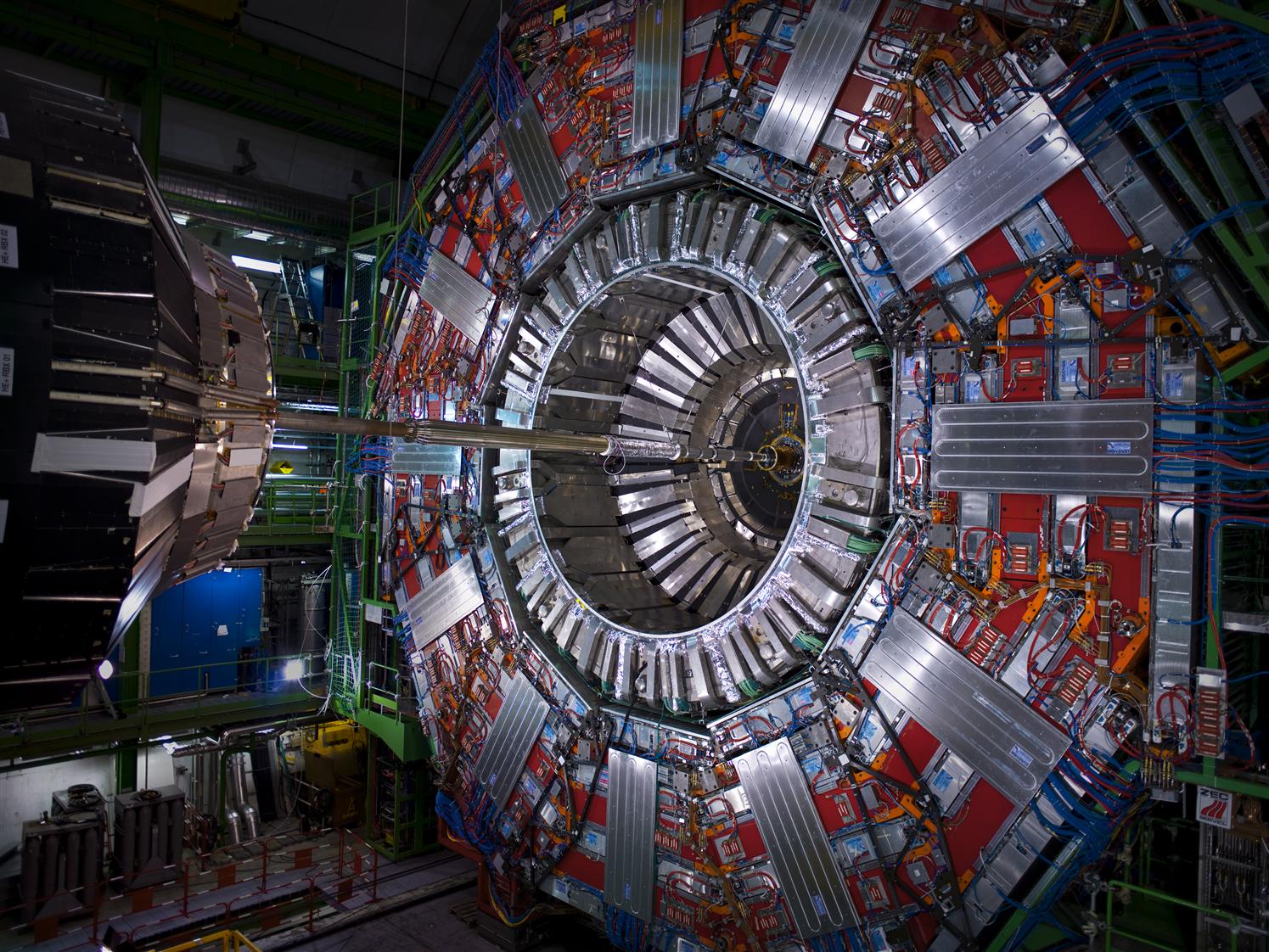
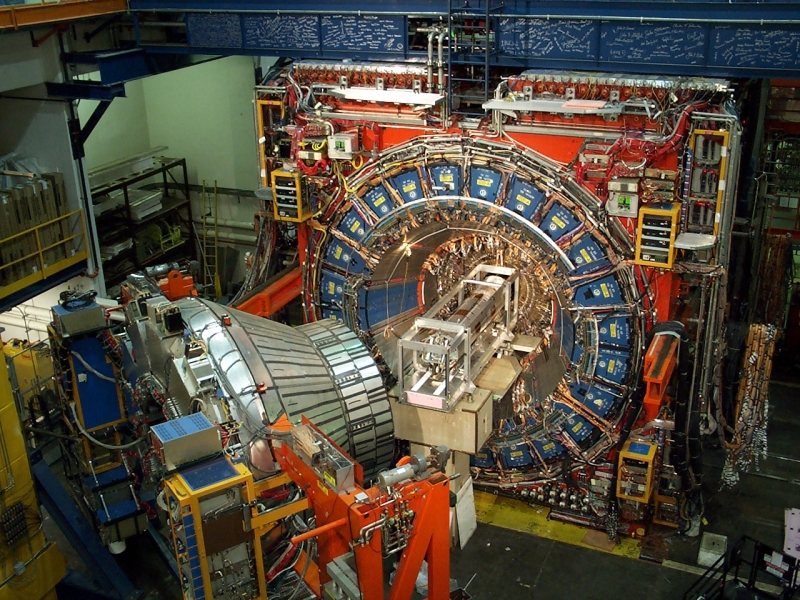
ATLAS is one of the four major experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN. It is a general-purpose particle physics experiment run by an international collaboration and, together with CMS, is designed to exploit the full discovery potential and the huge range of physics opportunities that the LHC provides.
Source: https://atlas.cern/ ATLAS Experiment © 2021 CERN
ATLAS Experiment © 2021 CERN